Importance of Cooling Belts in Production
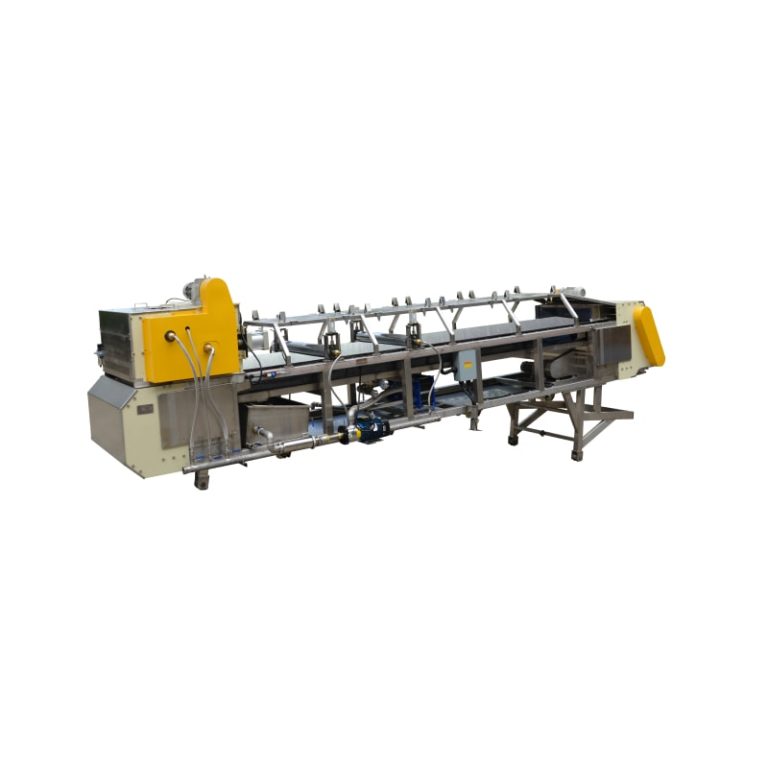
Cooling belts play an important role in the processing of coating powder manufacturing. Cooling belts are needed to cool thermos-melting compounds upon extrusion in order to provide for optimal processing and handling. The efficiency and success of the cooling process impact the quality of the final product. The use of a proper cooling belt is important for maintaining production quality and uniformity of chip size and thickness.
Overview of Cooling Belt Types
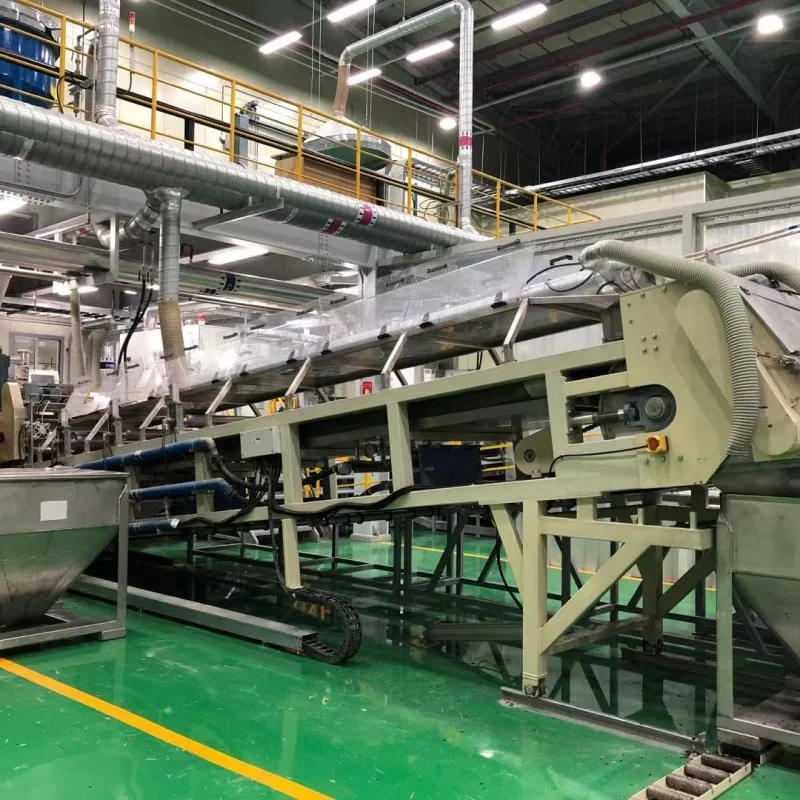

Stainless Steel Cooling Belt
Material Properties
Stainless steel cooling belt is world-famous due to its versatility to bear the temperature change. High-quality stainless steel band is utilized to accommodate dynamic tension force and temperature variation for a longer working period.
This makes it appropriate for the use in areas where repetitive work under high-pressure conditions is unavoidable.
Design Characteristics
Stainless steel cooling belt design features include a spray system of cooling water that effectively lowers the material temperature as the material passes along the conveyor.
Thickness of the chip can be adjusted while size is kept constant across to prevent contamination on the chips during the operation. Protection is ensured by a highly integrated protection mechanism to enhance reliability and facilitation in maintenance.
Air Cooling Belt (Slat)
Design Features
Air Cooling Belt (Slat) comprises cooling rollers, stainless steel slat chain conveyor, crusher, and cooling-air system. As it is constructed, thermos-melting extruder material may be rolled into 1-2mm-thick sheets using cooling rollers.
It is cooled to the ambient temperature on the stainless steel slat chain conveyor prior to crushing into chips and exit.
Operational Principle
This model operates primarily through air convection, which efficiently reduces material temperature without any contact with water or other coolants. Not only does this process ensure integrity of sensitive materials, but also ensures uniform chip size due to adjustable thickness settings.
Air Cooling Belt (Rubber)
Material Characteristics
The Air Cooling Belt (Rubber) consists of anti-static, heat-resistant, and flame-resistant simulated rubber. The design possesses flexibility and elasticity under variable conditions of manufacture and is aptly suited to the application of wide industrial uses.
Design Features
Its design involves a rubber conveyor that works together with cooling rollers, crushers, and cooling-air to manage temperatures effectively. The belt’s low energy consumption combined with its ease to maintain renders it a feasible option for the majority of producers seeking affordable alternatives.
Working Principles of Each Cooling Belt
Stainless Steel Cooling Belt
Heat Conduction Mechanism
The stainless steel cooling belt is founded on efficient heat transfer by conduction from its metal components. When the thermos-melting material is brought into contact with the chilled surface, heat is conducted away from the product rapidly, enabling rapid solidification into even chips for further processing.

Air Cooling Belt (Slat)
Convective Cooling Process
In contrast to conduction-based operations, air cooling belt (slat) employs convective methods where chilled air circulates around the product as it traverses along the conveyor.
The process minimizes direct contact with surfaces that potentially possess the capacity to change product properties while sustaining uniform ambient temperatures across processing stages.
Air Cooling Belt (Rubber)
Flexible Integration
The rubber air cooling belt is also easily integrated into existing systems due to its flexible design features. Its rubber surface can accommodate slight variations in product flow without compromising efficiency or effectiveness in cooling material temperatures by using convective airflow patterns similar to those used by slat models.
Comparative Analysis
Cooling Efficiency
Stainless steel cooling belt
In measuring the cooling capacity of various types of belts, there is a strong need to compare the suitability to your manufacturing set-up. Stainless steel cooling belts are at an advantage when handling high temperature surroundings because they feature good conduction of heat.
They dissipate heat fast away from the materials that undergo thermos-melting and then solidify faster and with proper chip formation.
Air cooling belt (slat)
The air cooling belt (slat) is, in comparison, employing the convective process of cooling. It blows cold air over the product on the conveyor and maintains constant ambient temperatures without surface contact touch. The method is very useful in ensuring that sensitive material maintains its integrity.
Air cooling belt (rubber)
The air cooling belt (rubber) offers flexible integration into current systems. Its flexibility allows for efficient temperature reduction through convective airflow patterns similar to those used in slat models. Such flexibility allows for different industrial applications where changing production conditions are the norm.
Durability and Maintenance
Durability is also a significant factor to consider in a cooling belt selection. Stainless steel cooling belt is renowned for durability under pressure environments. The band made from high-grade stainless steel resists the dynamic tension force and heat change over years.
Different maintenance requirements exist with belt types. Maintenance and cleanliness are simple on air cooling belt (slat), and that is why it proves more trustworthy when it comes to precision cooling systems.
Similarly, the air cooling belt (rubber) is low on power consumption and simple maintenance procedures, making it a cost-efficient option for cost-conscious manufacturers.
Cost-Effectiveness
Cost-effectiveness both in initial investment and long-term operating costs. While the stainless steel cooling belt is more expensive to invest in because of its durable construction, its life can mean lower maintenance and replacement costs over the long term.
The rubber and slat air cooling belts offer competitive prices with their efficient designs and low power usage. Their sophisticated safety protection systems also assist in reducing potential downtime expenses due to equipment failure.
Industry Applications
Stainless Steel Cooling Belt: High-Temperature Environments
Stainless steel cooling belt is ideally applicable for applications requiring high temperatures and stable performance. Its ability to withstand harsh conditions has made it a darling in industries requiring reliable heat management systems.
Air Cooling Belt (Slat): Precision Cooling Requirements
Precision cooling applications are supported by the air cooling belt (slat) due to its convective process which does not involve direct contact with surfaces. This feature prevents sensitive materials from altering their desired properties during processing processes.
Air Cooling Belt (Rubber): Flexible and Customizable Cooling Needs
For applications that need adjustable and flexible cooling, the air cooling belt (rubber) offers a flexible solution. It is flexible to allow for seamless integration into existing systems while effectively managing temperature fluctuation in different production conditions.
Selection Guide
Assessing Production Requirements
Temperature Control Specifications
Understanding your production temperature control needs is critical in deciding on a cooling belt model. Higher-temperature operations may better be served by stainless steel models, whereas ambient control requirements where precision is desired can use air-based options in the form of slat or rubber belts.
Space and Layout Considerations
Space limitations and availability also contribute to selection decisions. Compact designs may prefer air cooling belts due to their slender constructions with easy incorporation capabilities without heavy spatial demands over the more substantial stainless steel variants.
Budget Considerations
Pricing and Future Expenses
Traded against initial purchase cost for potential future expenses is an effective method to aid in establishing total cost-effectiveness in selecting an adequate model to suit your particular financial climate within your operations.
Overview of Cooling Belt Applications and Attributes
Stainless Steel Cooling Belt
Ideal for hot conditions with heavy-duty construction that ensures long-term performance.
Air Cooling Belt (Slat)
Ideal for high-precision applications requiring minimizing surface contact in convective processes.
Air Cooling Belt (Rubber)
Offers flexibility in system integration with effective temperature control under varying conditions.
Yuanli MPM Machinery Co., Ltd. focuses on researching and developing high-precision, intelligent, efficient, and environmentally friendly powder coating production machinery. It possesses numerous patents and certificates at home and abroad, including ISO9001, CE, and ATEX. The products of MPMtek enjoy a good reputation for their satisfactory performance, favorable price, and long-term stability, and have served many domestic and foreign customers.